Can Bees Damage Your Home’s Insulation? Prevention and Solutions

Bees are among the most vital creatures in nature, playing an essential role in pollination and biodiversity. However, while their ecological importance cannot be overstated, their presence inside human structures can lead to costly home maintenance issues. Homeowners often overlook the fact that bees, despite their small size, can compromise insulation, wiring, and even structural integrity. When left unchecked, bee infestations in walls, attics, or crawl spaces can escalate from minor inconveniences to severe home damage. Understanding how bees interact with insulation materials and implementing timely preventive measures ensures both home safety and ecological preservation.
How Bees Choose Insulated Spaces for Nesting
Bees are instinctively drawn to enclosed, warm, and dry environments that offer protection from predators and weather. Insulated spaces in homes, such as wall cavities and attics, often meet these ideal conditions. Fiberglass, foam, or cellulose insulation provides a soft and stable medium that bees find suitable for building hives. Once bees enter through small exterior gaps or vents, they establish colonies within these insulated voids, where temperatures remain stable year-round. Over time, hive expansion can lead to insulation compression, moisture buildup, and the deterioration of surrounding materials.
The scent of wax and honey produced by an established colony also attracts more bees, encouraging further nesting activity. Unlike other insects that may occupy visible spaces, bees prefer hidden areas where they can remain undisturbed. Unfortunately, this behavior often makes detection difficult until significant damage has occurred. A faint buzzing behind walls or a sweet odor may be the first indication that bees have made a home within insulation layers. Recognizing these early warning signs can prevent extensive repairs and ensure that necessary steps are taken before the infestation spreads further.
The Impact of Bees on Insulation Materials
Different insulation materials react uniquely to bee activity, depending on their composition and placement. Fiberglass insulation, for example, offers a lightweight and fibrous texture that bees can easily navigate and manipulate when forming hives. Foam insulation, though denser, often contains small air gaps that can become entry points for worker bees. Once a hive forms within these areas, the insulation’s thermal performance begins to degrade, leading to temperature inconsistencies throughout the home.
The constant presence of bees can also generate localized heat within wall cavities. The warmth from their collective activity and honey production affects insulation density, reducing its ability to maintain internal climate stability. Over time, the combined effects of moisture, heat, and honey residue can lead to higher energy bills as homeowners compensate for lost insulation efficiency. Moreover, if bees die within the walls, decomposing matter may release unpleasant odors that further compromise indoor air quality.
Importance of Expert Intervention
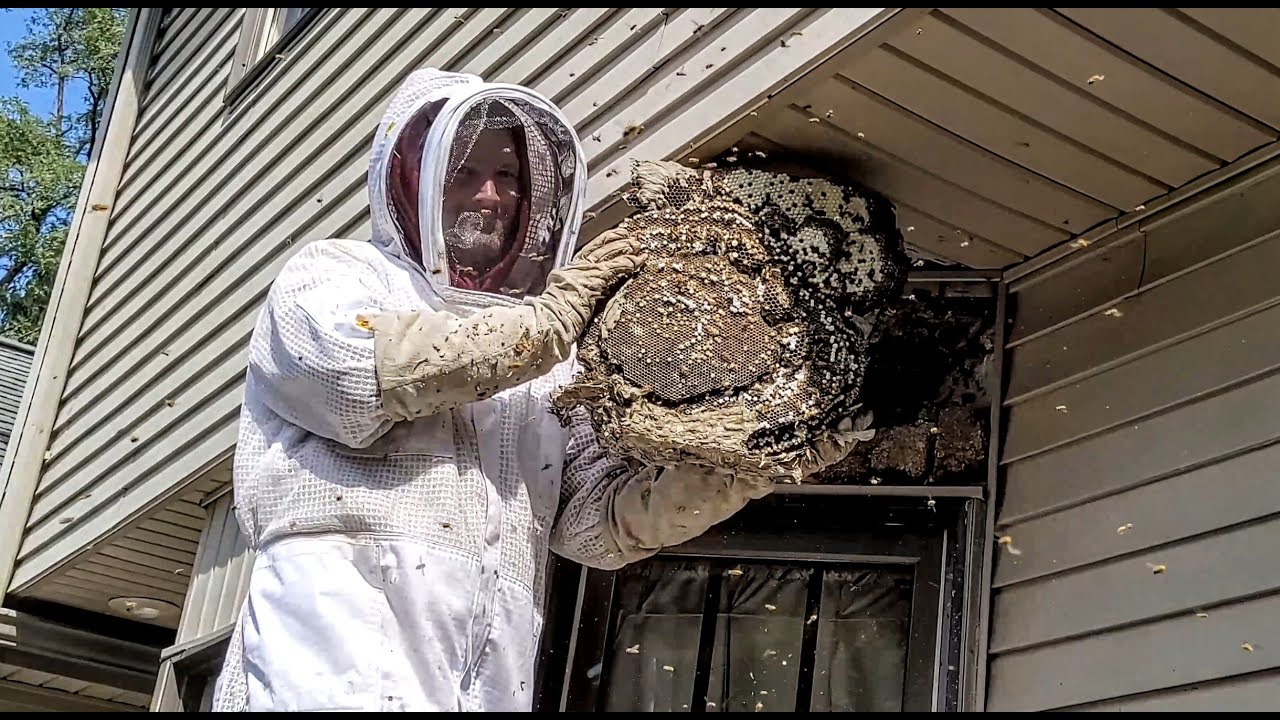
Attempting to handle a bee infestation independently can be both dangerous and ineffective. Without proper tools and safety protocols, removing bees from insulated structures poses significant risks, including stings and potential allergic reactions. Additionally, untrained handling may disrupt the hive in ways that spread bees throughout the property, making containment even more challenging. Engaging experts who understand bee behavior and structural dynamics ensures that removal efforts are both efficient and sustainable.
For instance, homeowners who require a residential bee removal service in Los Angeles benefit from specialists experienced in managing infestations in urban and suburban environments. These professionals not only remove active colonies but also assess insulation quality and recommend preventive sealing techniques. Their holistic approach ensures that homes remain protected against future nesting attempts while maintaining ecological balance. This method aligns with sustainable home management practices, emphasizing both safety and environmental stewardship.
Strategies for Bee-Proofing Home Insulation
Effective prevention begins with identifying and sealing all potential entry points around the property. Bees typically access insulation through small openings in soffits, eaves, or vent gaps. Regular maintenance and inspection of these vulnerable areas significantly reduce the likelihood of intrusion. Using fine mesh screens over ventilation outlets and ensuring proper caulking around windows and siding are practical first steps.
Homeowners should also consider the placement of flowering plants near the property. While bees are essential pollinators, minimizing the concentration of bee-attracting flora near exterior walls can discourage nesting attempts. Instead, cultivating low-pollen plants like ferns, hostas, or hydrangeas around the home provides beauty without inviting excessive bee activity. Maintaining clean and debris-free surroundings further eliminates potential hive-building materials that might attract foraging bees.
Balancing Bee Conservation with Home Protection
While the potential for bees to damage insulation exists, it’s equally important to recognize their irreplaceable ecological value. Bees are essential pollinators responsible for maintaining the balance of ecosystems and supporting global food production. Therefore, managing bee infestations should always emphasize humane and environmentally responsible solutions. Removing bees without extermination ensures their survival and continued contribution to natural pollination cycles.
Creating bee-friendly zones away from residential structures can help maintain harmony between home safety and environmental responsibility. Establishing dedicated pollinator gardens in open spaces or community areas allows bees to thrive without threatening household structures. These spaces provide nectar-rich plants that attract bees while keeping them away from insulation or wall cavities. This strategy not only safeguards homes but also fosters biodiversity within the local ecosystem.
Final Words
Bees, though essential to the environment, can inadvertently cause significant damage when nesting within home insulation. Their preference for warm, enclosed spaces makes insulation an attractive location, leading to potential structural and energy efficiency issues. Homeowners must understand the risks associated with bee infestations and take proactive steps to prevent them. Professional intervention remains the most reliable solution, ensuring safe removal and long-term prevention without compromising ecological values.
Through thoughtful planning, sustainable construction, and regular inspections, homeowners can maintain safe, energy-efficient spaces that coexist harmoniously with the natural world. By embracing both protection and conservation, modern homeowners contribute to a future where human comfort and environmental stewardship thrive side by side.